
The Dillian Loop
-
 Jared Dillian
Jared Dillian
- |
- March 10, 2016
- |
- Comments
So let’s take Japan, for example. Japan does quantitative easing.
-
If it works, it is declared a success and they do more.
-
If it doesn’t work, it means they need to do more.
Japan has done a lot of quantitative easing.
I’ll give you another one. Dodd-Frank was really meant to prevent bond traders from earning a million dollars. It has been successful, but as an unintended consequence, it has reduced liquidity. Now the SEC is regulating mutual funds even more to address the liquidity problems.
-
If the regulations work, they are declared a success and they write more regulations.
-
If they don’t work, it means they need to have more regulations.
You find many examples of these negative feedback loops in today’s markets. Policymakers will keep doing the same dumb stuff even though it makes the problem worse. It is like they are stuck in some recursive do-loop in Applesoft Basic.
I will call this The Dillian Loop.
Why This Happens
There are a couple of reasons why this happens. The biggest is that policymakers hate losing face more than anything. They are unwilling to admit that a course of action is bad, so they will keep slamming on the square peg to get it in the round hole over and over again until the hammer breaks.
There are countless more examples. Raising taxes raises progressively less revenue, so consequently, you raise taxes even more. You keep doing what doesn’t work, even if it doesn’t work.
This is allegedly an Einstein quote: “The definition of insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.”
The problem is, there are no controlled experiments in finance. Japan will never know how things would have worked out without Abenomics. Publicly, they will say it would have been worse. But there is no way to know!
After all, see how Depression-era history is taught in the United States. The New Deal saved the world. What if we didn’t have the New Deal? Maybe things would have been better? After all, the crash happened in 1929 and the economy didn’t recover until 1946. Warren Harding’s response to the (very severe) recession of 1921 was to do nothing, and the economy recovered in less than two years.
Interventionism is always praised after the fact. Nobody ever says doing nothing did something.
Like what you're reading?
Get this free newsletter in your inbox every Thursday! Read our privacy policy here.
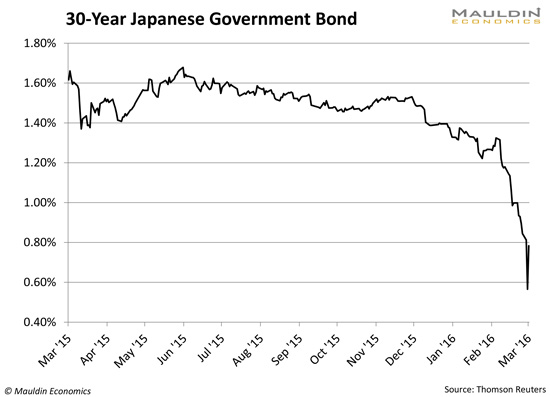
Japan is dealing with some pretty serious consequences of its interventionism. JGB yields dropped 25 basis points in a day, flattening the yield curve and rendering the banks possibly insolvent (and then went back up 24 hours later).
The Dillian Loop is really just an elaborate argument for laissez-faire, the idea that constant interventionism in a complex system yields results that are highly unpredictable and often deleterious. In this writer’s opinion, the best possible response to the housing crash, the financial crisis, the Great Recession, would have been to do—nothing.
Liquidity Gone, Never to Return
Back when I was trading 10 years ago, liquidity was abundant. You could sell infinite amounts of stuff without having any impact at all. Bond desks nowadays are reduced to trading odd lots and sitting around the rest of the time, while compliance reads their email.
You can regulate the markets a million different ways, but the last thing you want to do is screw with liquidity (a financial transactions tax would reduce what’s left of the capital markets to rubble). The government doesn’t realize that it alone is responsible for the liquidity problems and that additional regulation will only serve to reduce liquidity even more. I wouldn’t be surprised if 40 Act high yield mutual funds disappeared in a few years, which by the way, would mean a higher cost of capital for everyone.
That can’t possibly have any negative economic consequences.
But since we are caught in the Dillian Loop, what is the chance that we will get out of it? I’d say very slim. I’d say we could easily spend another 10-20 years in the Dillian Loop. The only thing that gets you out of the Dillian Loop is when you reach rock bottom, the point of maximum pain, and people are so disgusted with years of ineptitude that they are willing to try something different.
They might even get so desperate, they will try capitalism.
subscribers@mauldineconomics.com

 Jared Dillian
Jared Dillian